Gynecologic emergencies
Menometrorrhagia : useful imaging
High or menometrorrhagic genital hemorrhages are secondary to the presence of a uterine abnormality, more rarely annexed, and are an important reason for consultation in gynecology.
The 2 anatomical components of the uterine body (endometrium and myometer) are the site of multiple pathological processes that cause bleeding.
Pelvic ultrasound is the examination 1th intention. Pelvic MRI will be performed secondarily based on the results of ultrasound, or even hysteroscopy.
Endometric pathology
Atrophy
Of iatrogenic origin or due to menopause, the endometrium is barely visible on either side of the cavitary line(1). A thickness of the endometrium < 5 mm leads to the suspension of hysteroscopy (Figure 1). It would only be offered in the event of a recurrence of metrorrhages. Below this threshold, the risk of endometrial cancer in a menopausal woman with metrorrhages is less than 1%(1).
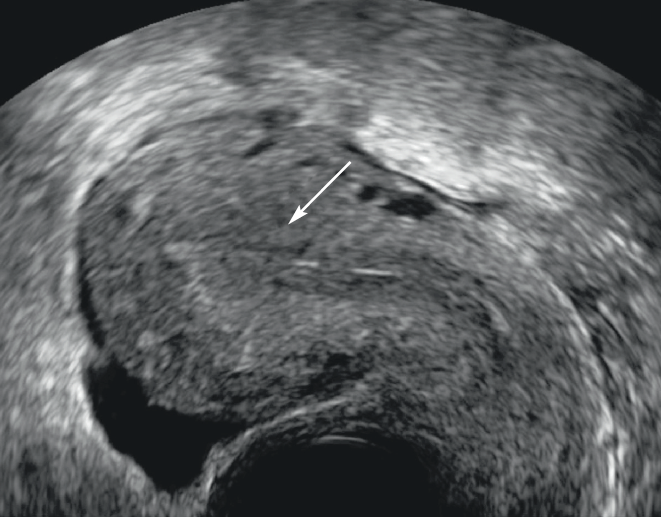
Figure 1: Atrophy of the endometrium. Sagittal cut in pelvic ultrasound by endovaginal means. The thickness of the endometrium is fine, measured at less than 5 mm (arrow).
Hypertrophy
In relation to hyperestrogeny, the diagnosis is referred to as a thickening of the endometrium > 15 mm in the period of genital activity and > 5 mm in the menopausal woman with or without hormone replacement treatment(2-5).
Endometer hyperplasia (anatomopathological term) is an exaggerated development in the number and density of endometrial glandular cells, ranging from simple hyperplasia to atypical hyperplasia.
The endometrium is hyperechogenic, homogeneous, or siege of small cystic formations. The endometrium-myometer interface is regular (Figure 2)(5). Doppler color or energy eliminates differential diagnosis, including the search for a polyp vascular pedicule(6). The ultrasound elements for endometrial cancer are(7):
- The heterogeneous appearance of the endometrium with hypoechogenic ranges and irregular contours;
- Endometric hypervascularization is observed more frequently in cancers (81%) than in benign lesions (12%), with a possible record of Doppler arterial flows more frequent in cancers;
- evaluation of the regularity of external contours contributes to the assessment of tumor extension: a regular-contours tumor is an element in favor of its limited character to the uterine cavity; on the other hand, irregular contours or myometer amputation favor a deep extension(8).
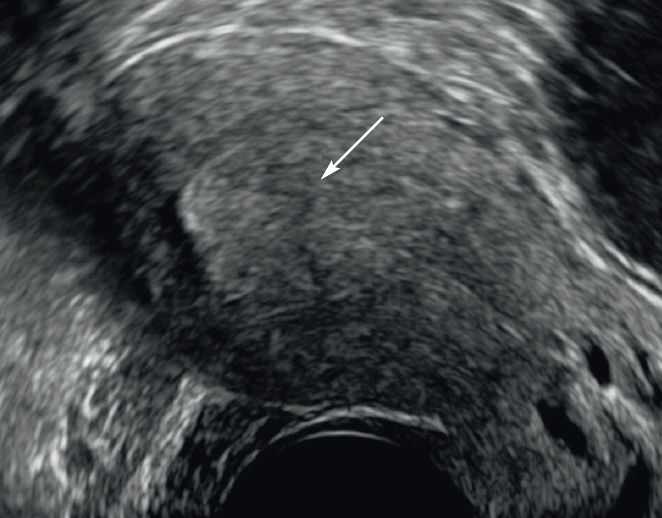
Figure 2: Endometer hypertrophy. Sagittal cut in pelvic ultrasound by endovaginal means. Presence of homogeneous thickness of the endometrium to more than 15 mm with some microcystic images (arrow).
Biopsy hysteroscopy remains essential to confirm diagnosis. MRI has a priori no indication in this benign pathology unless hysteroscopy is impossible (cervical stenosis). In this case, a pelvic MRI may be proposed to attempt to characterize endometrial thickening (Figure 3). The diffusion sequence differentiates benign endometrial lesions from endometrial tumors with a cut off < 1.05.103 mm2/s for tumors (Se: 96%, Sp: 95%). Myometrial infiltration and the heterogeneity of the tumor are also arguments in favor of a malignant origin(8).
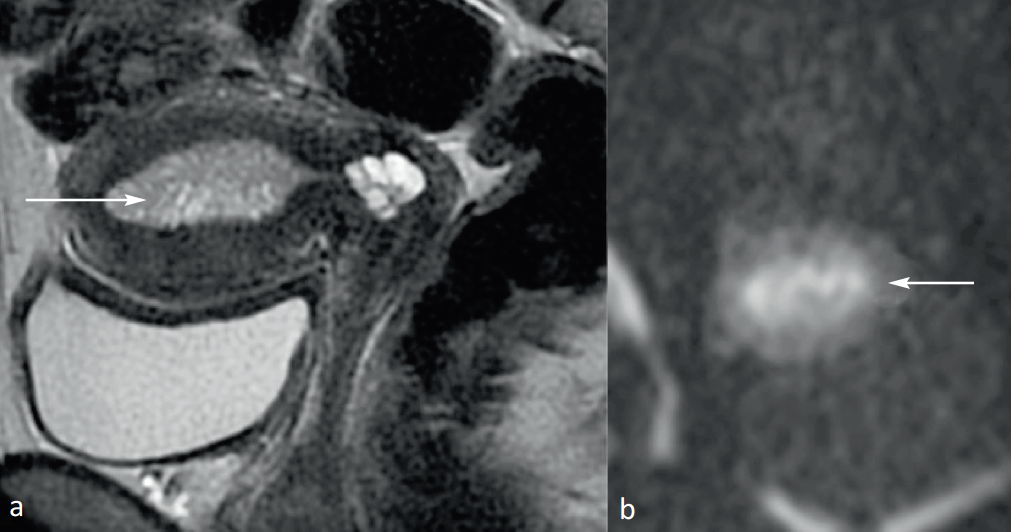
Figure 3: Endometer hypertrophy. Weighted Sagittal Cup in TSE T2. Endometer thickening in intermediate T2 signal, microcystic (arrow). (a) Fine cuts perpendicular to the body of the uterus in diffusion. No endometrial signal anomaly (arrow head) with ADC measured at 1.5 (b).
Polyps
They consist of endometrial glands and stroma and have a vascular pedicula. Revealed by menometrorrhagia, they are more common between 40 and 50 years. Their postmenopausal frequency is estimated at 16.3%, of which 43.6% are asymptomatic(9.10).
Enovaginal ultrasound typically shows intracavity, limited, hyperechogenic formation (Figure 4).
The polyps are about 3 to 30 mm long and are pediculated, which can then be used to go to the isthmus or endocol. They expand the uterine cavity, turning it back locally without interrupting the cavitary line. The larger ones remain hyperechogenic and very limited, but very frequently contain cystic glandular areas. Sometimes the polyp is old, calcified.
MRI is not recommended. However, it may be useful to know the nature of an abnormality in the uterine cavity when an MRI assessment is requested for other reasons. The polyp results in a T2 signal formation, normally lower than the healthy endometrium, due to a larger stromal component, with a T2 hyposignal range in fibrous areas or T2 hypersignal areas if there are small cysts within the polyp (Figure 5). The injection of dynamic gadolinium can highlight the polyp pedicula with its central vessel, with a moderate, even marked contrast take on later cuts. CDA (Apparent Diffusion Coefficient) is useful in differentiating a mild polyp (ADC > 10-3 mm2/s) from a cancer (CDA < 10-3 mm2/s). Leiomyoma, which has a T2 signal significantly lower than the healthy endometrium on T2-weighted sequences, is readily identified in MRI(8).
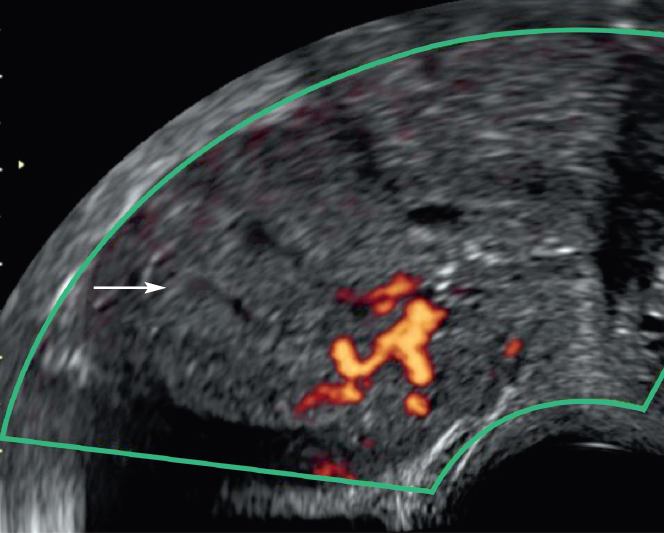
Figure 4: Endometer glandulo-cystic polyp. Sagittal cut in pelvic ultrasound by endovaginal means. Microcystic endometrial thickening (arrow) with vascular pedicule visible in doppler energy.
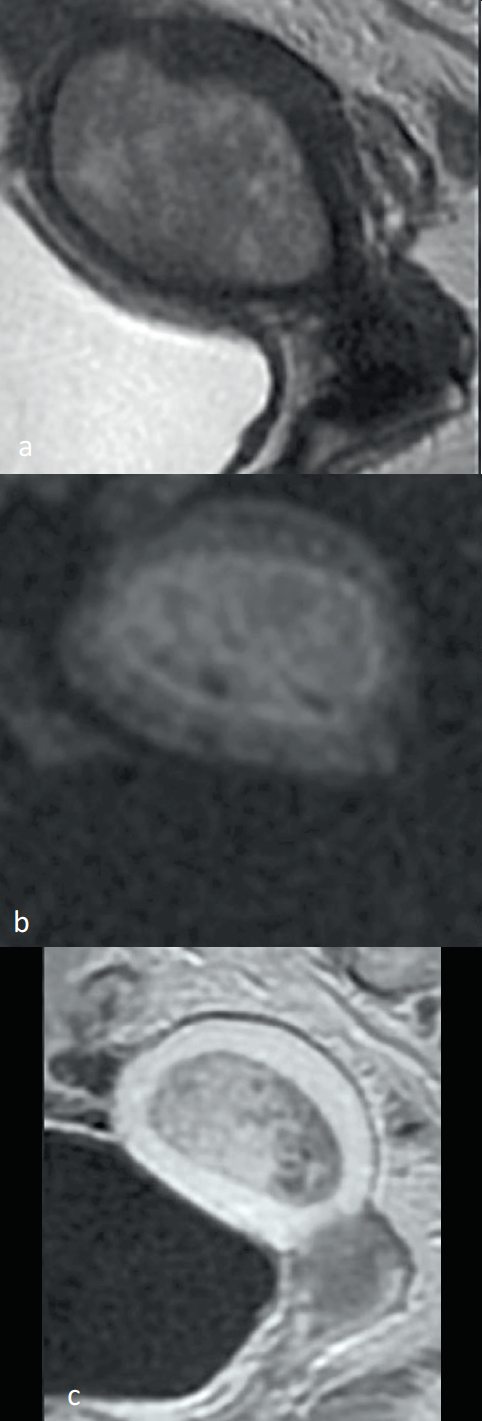
Figure 5: Endometer glandulo-cystic polyp. Weighted Sagittal Cup in TSE T2 (a), fine cut perpendicular to the body of the uterus in diffusion, Sagittal Cup T1 after injection of gadolinium (c). Intermediate T2 signal endometrium lesion (a), without diffusion signal abnormality (b). The endometrium interface is regular.
Endometer under tamoxifene
The beneficial effect of tamoxifen on the life expectancy of women with breast cancer is well documented. Tamoxifen, along with its antiestrogen effects on breast tissue, has an estrogen-like effect on the uterus.
Tamoxifen is responsible for imaging(11-13):
- a microcystic hyperechogenic thickening of the endometrium (Figure 6). At the anatomopathological level, the endometrium produces the appearance of glandulo-cystic atrophy; the apparent thickening of the endometrium is the summation of glandular cysts covered with an unstratified thin epithelium;
- the development of mucous polyps;
- development of endometrial cancer. This risk would be multiplied by 1.6.
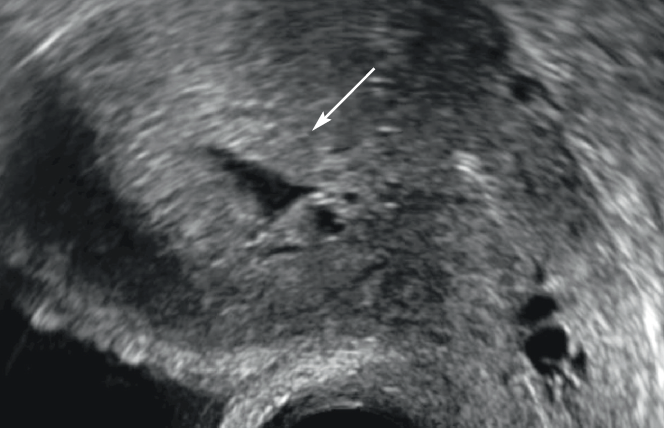
Figure 6: Glandulo-cystic acid of the endometrium under tamoxifen. Sagittal cut in pelvic ultrasound by endovaginal means. Microcystic endometrium thickening (arrow).
Echographic signs persist after treatment is stopped, with the endometrium not renewed in menopausal patients.
Tamoxifen also had an effect on the myometer with an increase in the size of the myomas and a reactivation of the adenomyose outbreaks. Antiaromatase treatments in breast cancer, however, do not have an effect on the uterus.
|
Myometrial pathology
Myomas
Uterine leiomyomas are the most common uterine tumors, present in 20-30% of women after 30 years, more common in black patients and globally present in 75% of hysterectomy(14).
Myomas are most often multiple (98%), developed mainly in the uterine body. The clinical presentation of myomas is very varied: asymptomatic, bleeding, pain, infertility or palpable pelvic mass. Menorrhagia is secondary to the presence of a submucosal myoma or a polymyomatous uterus.
The pelvic ultrasound
This is the first-line examination in the suspicion of uterine myoma. In ultrasound, a rounded structure with relatively regular edges is visualized, clearly differentiated from the normal adjacent myometer. The echolgenicity of myomes varies according to their reshuffling, the majority of myomes appear hypoechogenic, others have mixed echostructure more or less heterogeneous (Figure 7). The color or energy Doppler visualizes the presence of a significant peripheral or central vascularization of the myomes.
A number of myomas > 5, a large size of myomas > 3 cm, an intermediate position of the uterus or obesity significantly limit the quality of the examination.
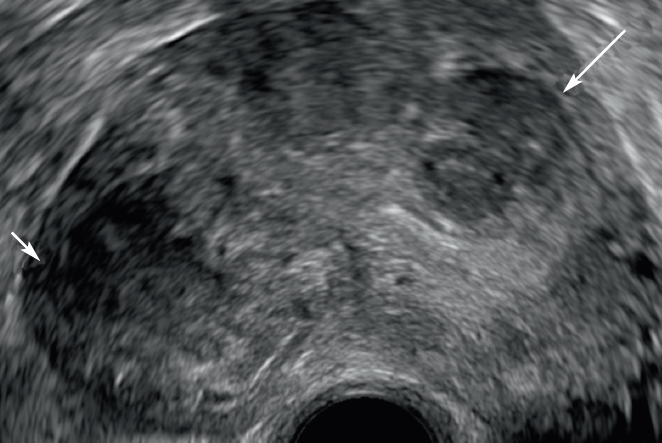
Figure 7: Polymyomatous uterus in endovaginal ultrasound. Enovaginal ultrasound cut in 2D mode visualizing a uterus of dented contours (arrows heads), with several circumscribed masses roughly rounded hypoechogenic compared to the residual healthy myometer corresponding to multiple interstitial myomas of types 3 and 4 (arrows).
In MRI
Un common uterine leiomyoma, there was a significant T2 hyposignal compared to the normal adjacent external myometer signal and a non-specific T1 isosignal (Figure 8)(15-17). Functional imaging is of no interest to common uterine myomas with a diffusion hyposignal and a type 2 enhancement curve, often modeled on the normal myometer while retaining the suboffset aspect. Late T1 shots after gadolinium injection showed a more or less homogeneous contrast take of the discreetly hypo-intense or iso-intense myoma compared to the adjacent myometer.
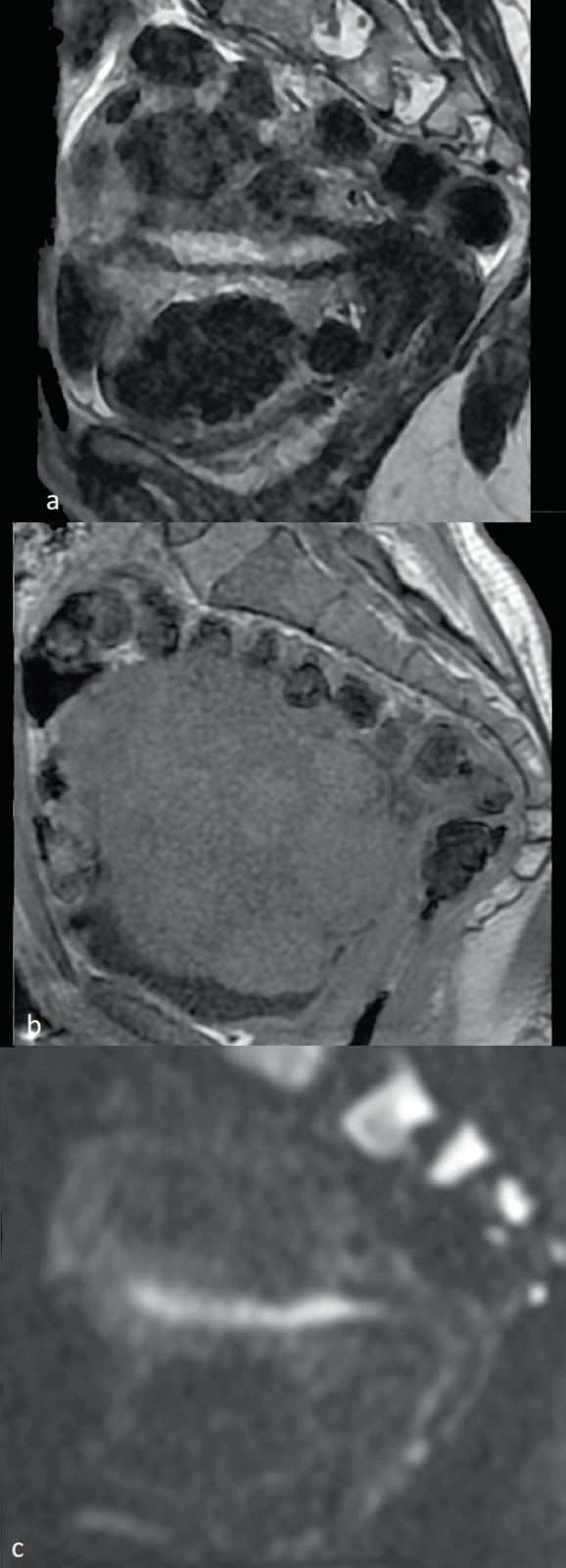
Figure 8: MRI of a polymyomatous uterus. MRI sequence in T2 (a), T1 (b), and b1 400 (c) visualizing a large uterus of lumpy edges, seat of multiple T2 hyposignal myomes and diffusion, and T1 isosignal.
The topography of myomasIt
It needs to be clarified in order to adapt the therapeutic management as best as possible. It appears necessary to use the new FIGO classification of leiomyomas also used by gynecologists (Figure 9)(19).
- Interstitial myomas ("types 3 and 4") developed exclusively in the myometer are the most common. The "type 4" myoma is circumscribed by normal residual myometer, while the "type 3" myoma appears within the endometrial mucosa without overadded mass effect.
- The intracavitarian myomas ("types 0, 1 and 2") develop from the myometer but have an intracavitarian component more or less developed repressing the endometrial mucosa. The FIGO classification differentiates fully intracavitarian "type 0" myomes with a broad or pediculated implantation basis. The myomes "type 1" and "type 2" have an intracavity component of > 50% and < 50%, respectively.
- Underserous myomas develop from the myometer, but have a more or less developed extra-uterine component. The FIGO classification differentiates myomas with an respective extra-uterine component < 50%, > 50% and 100% as "type 5, 6 and 7", respectively.
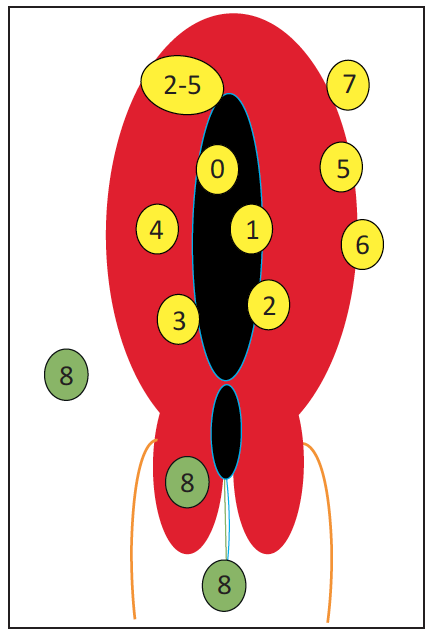
Figure 9: Schematic of topography of uterine leiomyomas with classification according to the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO): the body myomes are submucosal (0, 1, 2), interstitial (3, 4), transmurals (2-5), and subserous (5, 6, 7). Myomas that are not directly related to the myometer are type 8.
The reworked myomas
It is very difficult to characterize the Doppler-ultrasound myomes. It is MRI that will suggest the presence of possible reshuffles(14,16,17).
Hyaline fibrosis is the reshuffle found in most of the common myomas that cause their free T2 hyposignal with T1 isosignal.
The diffuse or focal oedematous reshuffle (50%) is responsible for An intermediate signal of the myoma in T2 and T1 weighting. Functional imaging is useful in differentiating an oedematous myoma from a cellular myome, which is crucial for management. Thus, the calculated value of the mean ADC within a hypersignal myoma diffusion in b1000 is significantly greater (> 1.6 10-3 mm2/s) than that of a cell myoma.
Myomas in cystic degeneration are rare since they represent about 4% of myomas.
Necessity Robiosis of a myome is secondary to the obstruction of the vessels on the periphery of the myome. This is facilitated by pregnancy or oral contraceptives. Contrary to other changes, hemorrhagic degeneration is symptomatic, causing acute pain. The MRI presentation is classic with a T1-weighted hypersignal and a T2 hyposignal corresponding to the thrombosis of the peripheral veins of the myoma.
Atypical myomas
The subtypes have specific histological characteristics that need to be differentiated from a possible leiomyosarcoma. These myomes are classified as cellular, hemorrhagic, epithelioid, myxoid, lipomatous, mitotically active, atypical or vascular. The vast majority of these specific myomes are benign, rarely uncertain and exceptionally malignant.
The point of imaging is to alert the surgeon to the atypical character of a myome(15-17).
Cellular leiomyoma
It represents the most frequently encountered histological subtype.
Histologically, it is defined by an increase in the number of cells per unit in comparison with the adjacent myometer and the majority of myomas.
In MRI, on morphological sequences, it presents an intermediate T2 signal that is globally homogeneous compared to the adjacent myometer, associated with a T1 isosignal. On diffusion sequences, there is a hypersignal on the high b values (b ≥ 1000 mm/sec2) associated with a reduction in the ADC coefficient for cell myomas, unlike oedematous myomas. Preliminary work suggests that the mean ADC value of cell myomes (1.18 x 10-3 mm2/sec) compared to oedematous myomes (1.610-3 mm2/sec) is significantly different in terms of differential diagnosis (Figure 10).
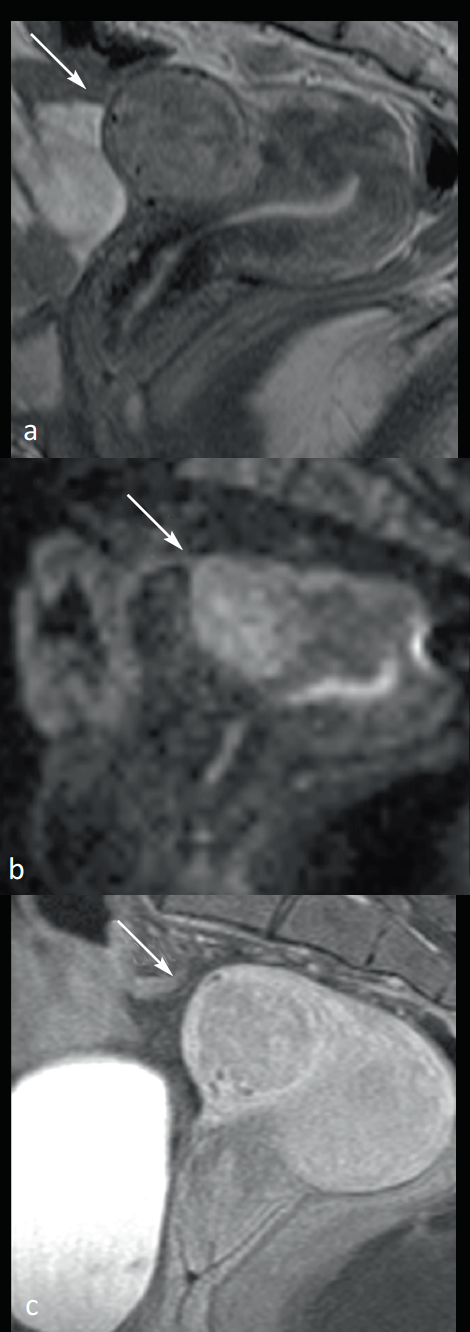
Figure 10: Benign cellular leiomyoma in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Weighted MRI cuts T2 (a), diffusion with b 1200 (b), T1 with grease suppression and gadolinium injection visualizing a 3-5 leiomyoma (arrows) in heterogeneous T2 intermediate signal, diffusion hypersignal, and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values between 1.26 and 1.5 10-3 mm 2/sec in relation to a cell leiomyoma.
Leiomyosarcoma
Leiomyosarcoma is a rare tumor representing 1.3% of malignant tumors in the uterus.
The histological criteria leading to diagnosis are the conjunction of high cellularity, numerous mitoses, and cytonuclear atypies.
They have irregular limits, with an intermediate T2 signal, heme content(18).
The diffusion sequences are therefore essential, they find a hypersignal on the high b values (b ≥ 1000 mm/s2) associated with a reduction in the ADC coefficient (Figure 11). However, there is no consensus to define a threshold value for formally differentiating cell myoma and leiomyosarcoma, which makes it desirable to combine all criteria. Some authors found overlap in ADC values, others found significantly lower ADC for leiomyosarcomas versus cell myomes (mean ADC: 0.79 10-3 mm2/s versus 1.18 10-3 mm(2/s).
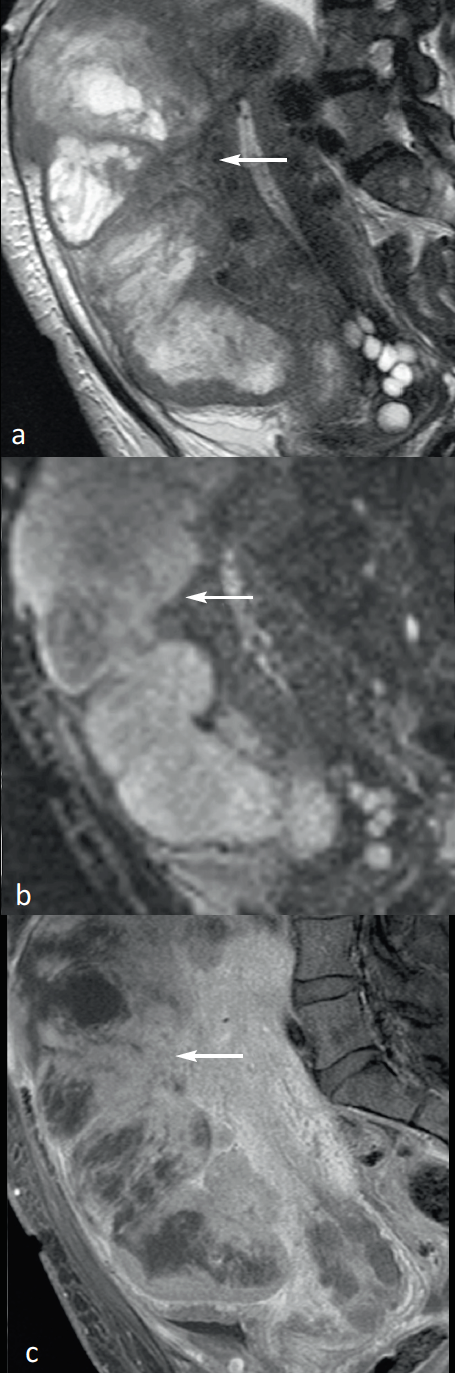
Figure 11: Uterine leiomyosarcoma in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). T2-weighted MRI cuts (a), diffusion to b1 200 (b) and T1 after gadolinium injection and fat suppression (c) visualizing a tumor mass (arrows) invading the anterior myometer. This mass has an excessively heterogeneous signal with a large tissue range in intermediate T2 (arrow), hyperdiffusion with ADC measured at 0.7 10-3 mm2/sec in relation to a high-grade uterine body leiomyosarcoma.
Criteria for suspicion of myometrial lesion:
|
Adénomyosis
Adenomyosis is excessively common; some studies have suggested prevalence figures for the disease between 30-47%.
Two-thirds of patients are symptomatic, with pelvic pain, dysmmenorrhea and menometrorrhagia. This symptomatology is non-specific and can be found in bleeding of functional origin, and especially in leiomyomas.
Age, management, parity, endometrial samples, iterative curetas, DES capture or subperitoneal endometriosis are ethopathogenic factors significantly associated with adenomyosis.
Adenomyosis is characterized by the presence of heterotopic endometrial mucosa within the myometer, surrounded by hypertrophy and secondary smooth muscle hyperplasia.
The two most common forms of adenomyosis are(20):
- The diffuse adenomyosis, the most common, corresponds to a reach of at least one myometrial sector (background, anterior, posterior, right, left). This can be asymmetric or global. Depending on its depth extension, the surface reach that is limited to the inner third of the myometer is differentiated from the deep reach that extends to the vascular arch (two-thirds internal) respecting a peripheral myometer collar.
- Adenomyoma is a nodular form; for this reason, when examining macroscopic pathological anatomy, it is difficult to differentiate from an authentic leiomyoma. Its elected seat is located around uterine horns and can be multiple and/or associated with diffuse adenomyosis.
Adenomyoma can sometimes cystize with a superconducting central cavity with hemorrhagic content.
In addition, it is important to differentiate between 2 types of adenomyoses, both internal and external. Internal adenomyosis corresponds to the diffuse adenomyosis described above. External adenomyosis corresponds to colonization of the myometer from outside within from extensive peritoneal endometriosis. It is characterized by muscle hyperplasia and fibrosis surrounding ectopic endometrial tissue.
Imaging (ultrasound and MRI) makes the diagnosis of adenomyosis in an easy and reliable way, allowing clinicians to take optimal therapeutic care.
Ultrasound and adenomyosis
Enovaginal ultrasound is the reference technique for asserting adenomyosis(21) (Figure 12).
Small anechogenic deficiencies (2-9 mm) in intramyometrial, often close to the endometrium-myometer interface, are the most specific (98%) but not very sensitive (50-65%). This indicates the presence of ectopic endometrial outbreaks within the uterine muscle. The color Doppler differentiates these gaps in vascular structures. Hyperechogenic nodules, juxta-endometrial hyperechogenic linear streaks giving a nodular or irregular aspect of the endometrium-myometer interface are also echographic arguments in favor of ectopic endometrial tissues.
The ultrasonic criteria that are secondary to the development of muscle hyperplasia are myometrial heterogeneity, hypochoetical linear streaks Genes and increase in uterus volume most often asymmetrical. Myometrial heterogeneity is the most commonly used sign for adenomyosis diagnosis. However, it is not specific (30-65%). Doppler energy differentiates diffused adenomyose and myomas. Adenomyosis has radiary vascularization, unlike myomas with circumferential peripheral vascularization(22).
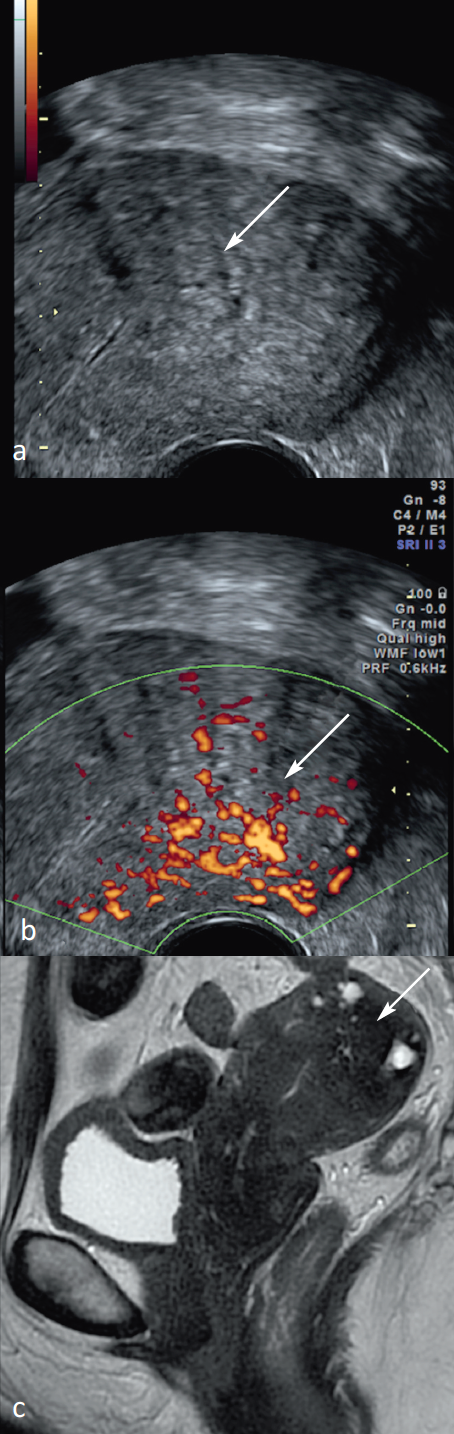
Figure 12: Association of signs of adenomyosis in endovaginal ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Echographic cuts in 2D mode (a) visualizing asymmetrical myometer hypertrophy, the regular global appearance containing myometrial cystic images (arrow) associated with poorly limited myometrial heterogeneity with radiary vascularization (arrow head) in Doppler energy (b). MRI Fast Spin Echo (FSE) sequences in 2D Sagittal T2 mode (c) visualizing a multitude of hyperintense spots, most of which are located throughout the thickness of the posterior myometer (arrow) in relation to an asymmetrical deep diffuse internal adenomyosis.
MRI and adenomyosis
MRI is always a second-line examination after pelvic ultrasound(23-25) (Figure 13).
• The thickness of the junctions is the most commonly used criterion; it corresponds histologically to muscle hypertrophy. A threshold ≥ 12 mm was associated with positive and negative sensitivity, specificity and predictive values of 0.93, 0.91, 0.79 and 0.98.
The first evaluating the ZJmax/myometer ratio, a ratio ≥ 40% was associated with positive and negative sensitivities, specificities and predictive values of 0.65 , 0,93, 0,81 and 0,84.
These criteria taken in isolation are not necessary and sufficient to make the diagnosis of adenomyosis.
• T2 hypersignal spots are the only pathognomonic criterion, but not very sensitive. These spots are most often seen in juxta-endometrial and more rarely in the depths of uterine muscle.
• The presence of haemorrhagic spots is much less frequent and the detection rate on T1 weighted sequences is low.
It is the combination of these various criteria that enables MRI to be a reference technique for this diagnosis.
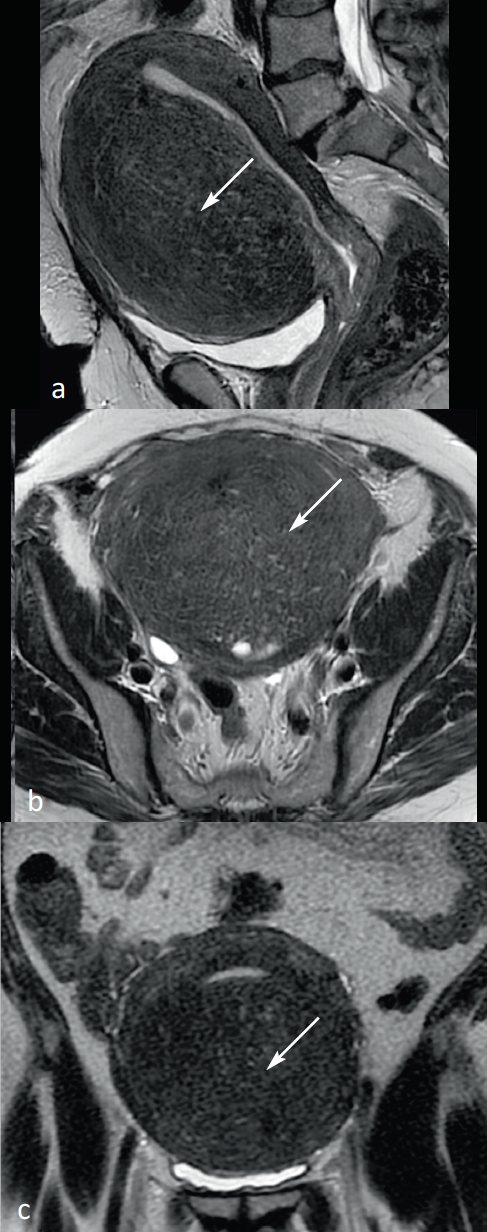
Figure 13: Hyperintense myometrial Spots in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). MRI Fast Spin Echo (FSE) sequences in 2D sagittal (a), axial (b), and coronal (c) mode, visualizing a multitude of hyperintense spots mostly located throughout the thickness of the myometer (arrows) in relation to a deep internal adenomyose.
Diagnostic criteria Adenomyosis MRI:
|
Conclusion
After clinical examination and possible biological samples, endovaginal ultrasound is the first-line examination in the etiological process of abnormal gynecological bleeding.The MRI completes the etiological balance of complex forms and/or difficult diagnosis.
References available on request at biblio@len-medical.fr
Articles on the same theme
- 1 of 2
- >